在 react 中可以通过 setState 来更新状态,重新渲染该组件及其子组件。react 15 在一次事务更新中,会合并多次状态更新(批量更新),等到事务结束再统一更新状态;而 react 16 中已经没有了事务的概念,在 Fiber 架构下,setState 是如何实现的呢?
写在前面
先看道面试题
// ...
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
val: 0
};
}
componentDidMount() {
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1});
console.log(this.state.val);
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1});
console.log(this.state.val);
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1});
console.log(this.state.val);
this.setState({val: this.state.val + 1});
console.log(this.state.val);
}, 0);
}
// ...
};上面代码的执行结果是
0
0
2
3直观点看,在 setTimeout 外面的状态更新是异步的,而 setTimeout 里的状态更新是同步的。说明 setState 更新状态并不总是异步的。当它处于 react 的生命周期钩子函数、合成事件,表现为异步;其他情况则表现为同步,比如 setTimeout 和原生事件等
本文会结合源码分析,总结下 react 15 和 16 两个版本关于 setState 的实现
react 15
react 15 是通过事务机制和锁来控制批量更新时机,实现“异步”更新
关键词:
- Transaction(事务)
- dirtyComponents
- isBatchingUpdates(锁)
Transaction
看下官方关于 Transaction 的注释:
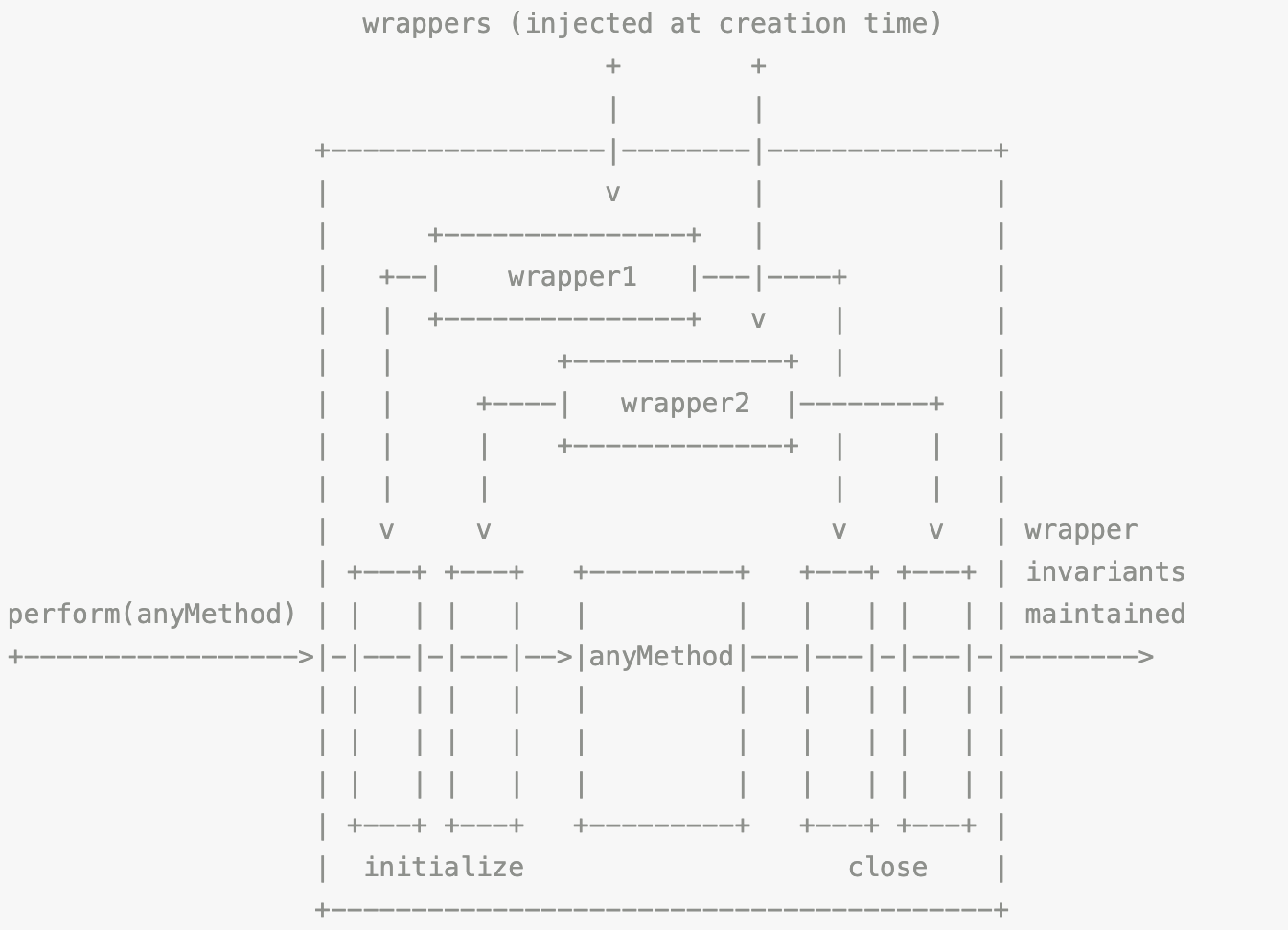
这个注释其实就是 Transaction 的核心功能,主要是包装要执行的函数 method(生命周期钩子函数或者 react 事件处理函数等),通过 Transaction.perform 来执行 method
下面是一个基础的 Transaction 对象,是 react 事务对象的父类
var Transaction = {
// 重置 Transaction,刷新之前的数据
reinitializeTransaction: function () {
// getTransactionWrappers 其实是一个获取wrapper的抽象方法,需要具体实现
// 用于获取当前事务需要的所有 wrappers
this.transactionWrappers = this.getTransactionWrappers();
if (this.wrapperInitData) {
this.wrapperInitData.length = 0;
} else {
this.wrapperInitData = [];
}
this._isInTransaction = false;
},
_isInTransaction: false,
getTransactionWrappers: null,
// 判断当前事务是否正在执行
// 可用于防止当前事务被打断
isInTransaction: function () {
return !!this._isInTransaction;
},
perform: () => {
// this._isInTransaction = true 表明正处于事务中
// this.initializeAll
// 执行method
// this.closeAll
// this._isInTransaction = false
},
initializeAll: () => {
// 遍历所有wrappers,执行initialize方法
}
closeAll: () => {
// 遍历所有wrappers,执行所有close方法
}Transaction 执行 perform 前,会先执行所有已注入的 wrapper 的 initialize 方法来初始化事务,执行完方法后再调用 wrapper 的 close 方法来结束事务
setState
setState 的执行流程如下:
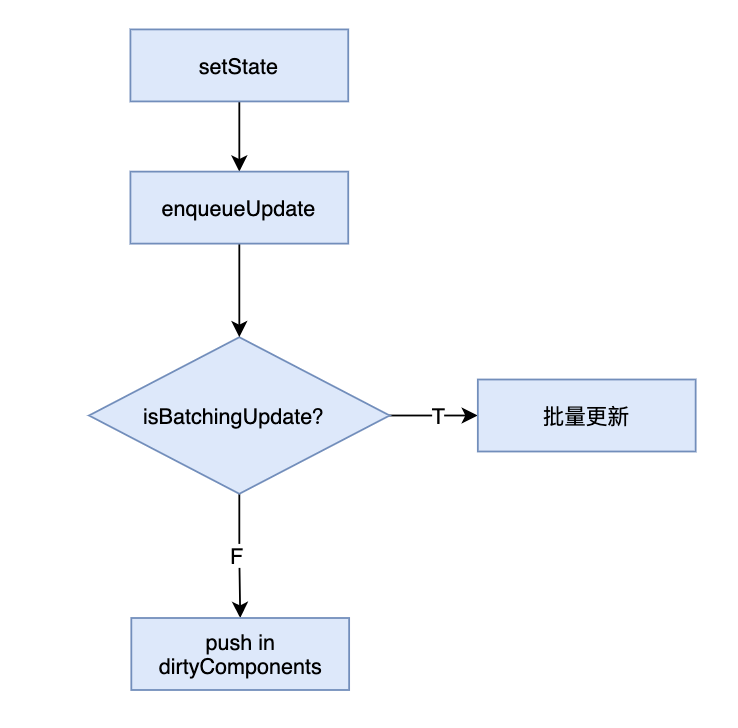
看下源码:
ReactComponent.prototype.setState = function(partialState, callback) {
this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState);
if (callback) {
this.updater.enqueueCallback(this, callback, 'setState');
}
};
// ...
enqueueSetState: function(publicInstance, partialState) {
var internalInstance = getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate(
publicInstance,
'setState',
);
var queue =
internalInstance._pendingStateQueue ||
(internalInstance._pendingStateQueue = []);
queue.push(partialState);
enqueueUpdate(internalInstance);
},
// ...
function enqueueUpdate(internalInstance) {
ReactUpdates.enqueueUpdate(internalInstance);
}
// ...
function enqueueUpdate(component) {
// ...
if (!batchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates) {
batchingStrategy.batchedUpdates(enqueueUpdate, component);
return;
}
dirtyComponents.push(component);
}假设现在触发了一次 react 的点击事件,并执行 setState ,此时 setState 处于 react 的更新事务流程中。开始执行事务时会设置 isBatchingUpdates 为 true,表示当前事务处于批量更新过程(锁住这个状态),导致后续加入的 setState 只会加入 dirtyComponents 中,等到事务 close 后,将 isBatchingUpdates 设置为 false,执行 batchingStrategy.batchedUpdates 合并全部状态,再更新。
react 中有一个更新策略对象 ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy,主要用于维护批量更新状态(isBatchingUpdates)和启动更新事务(batchedUpdates)
// 更新事务的 wrappers
var TRANSACTION_WRAPPERS = [FLUSH_BATCHED_UPDATES, RESET_BATCHED_UPDATES];
// 修改批量更新状态
var RESET_BATCHED_UPDATES = {
initialize: emptyFunction,
close: function () {
ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates = false;
}
};
// 遍历所有的 dirtyComponents 更新组件
var FLUSH_BATCHED_UPDATES = {
initialize: emptyFunction,
close: ReactUpdates.flushBatchedUpdates.bind(ReactUpdates)
};
// ...
// 更新策略对象
var ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy = {
// 是否批量更新
isBatchingUpdates: false,
batchedUpdates: function (callback, a, b, c, d, e) {
var alreadyBatchingUpdates = ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates;
ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates = true;
if (alreadyBatchingUpdates) {
return callback(a, b, c, d, e);
} else {
return transaction.perform(callback, null, a, b, c, d, e);
}
}
};
// ...
// 更新事务对象,是 Transition 对象的子类
function ReactDefaultBatchingStrategyTransaction() {
// 初始化事务
this.reinitializeTransaction();
}
// ...
// 实现了 getTransactionWrappers 这个抽象方法,即注入更新事务的 wrappers
Object.assign(ReactDefaultBatchingStrategyTransaction.prototype, Transaction, {
getTransactionWrappers: function() {
return TRANSACTION_WRAPPERS;
},
});
...
var transaction = new ReactDefaultBatchingStrategyTransaction();从源码可以看到,setState 会调用 ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy.batchedUpdates,从而执行 transition.perform 开启更新事务
react 16
react 16 引入了 Fiber 架构,抛弃了 react 15 的事务机制,借助锁和更新链表实现批量更新
关键词:
- updateQueue(状态更新队列)
- isBatchingUpdates(锁)
react 16 的组件渲染过程主要分为 render 阶段和 commit 阶段,从执行 setState 开始看下两个阶段都做了什么
主要执行流程如下:
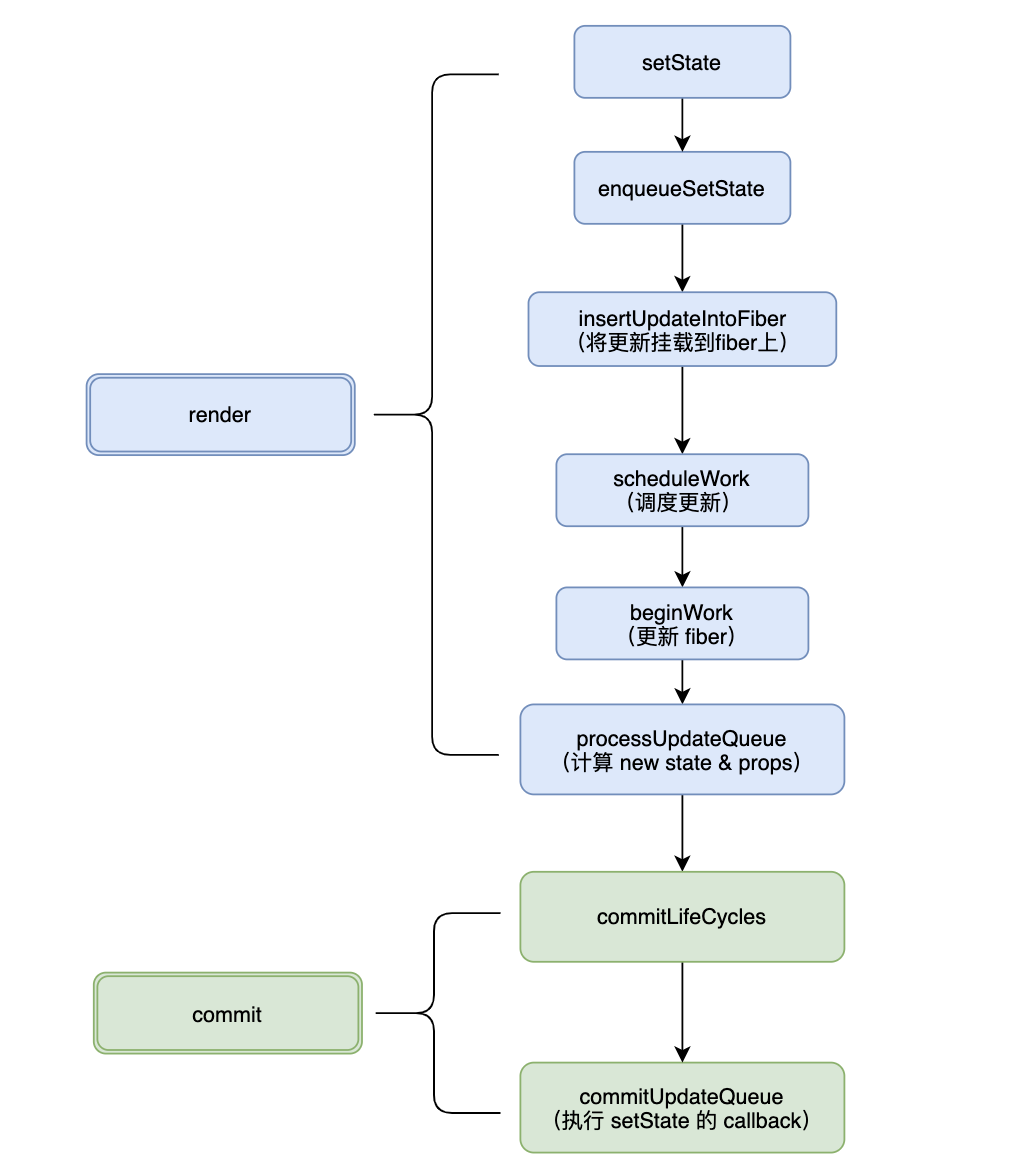
以下源码参考自 v16.8.3
render
这个阶段主要是收集各个 fiber 节点上的更新,将它们追加到 updateQueue 上
// react/packages/react/src/ReactBaseClasses.js
Component.prototype.setState = function (partialState, callback) {
// ...
this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState, callback, "setState");
};
// react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberClassComponent.js
const classComponentUpdater = {
// ...
enqueueSetState(inst, payload, callback) {
const fiber = getInstance(inst);
const currentTime = requestCurrentTime();
const expirationTime = computeExpirationForFiber(currentTime, fiber);
// 创建一个更新队列
const update = createUpdate(expirationTime);
update.payload = payload;
if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) {
// ...
update.callback = callback;
}
// TODO 暂不清楚这个的具体作用
flushPassiveEffects();
// 将更新任务挂载到 fiber 上
enqueueUpdate(fiber, update);
// 调度更新
scheduleWork(fiber, expirationTime);
},
// ...
};
// react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactUpdateQueue.js
export function enqueueUpdate<State>(fiber: Fiber, update: Update<State>) {
// Update queues are created lazily.
const alternate = fiber.alternate;
let queue1;
let queue2;
// ...
{
appendUpdateToQueue(queue1, update);
}
// ...
}
// ...
function appendUpdateToQueue<State>(
queue: UpdateQueue<State>,
update: Update<State>
) {
// 将 update 对象挂载到更新队列 updateQueue 上,形成一个环状单向链表
if (queue.lastUpdate === null) {
queue.firstUpdate = queue.lastUpdate = update;
} else {
queue.lastUpdate.next = update;
queue.lastUpdate = update;
}
}render 阶段,在更新单个 fiber 时(beginWork),会遍历更新队列计算得到最新的 state,该操作由 processUpdateQueue 完成。状态更新过程的调用栈有:beginWork -> updateClassComponent -> updateClassInstance -> processUpdateQueue
// react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactUpdateQueue.js
function updateClassInstance(
current: Fiber,
workInProgress: Fiber,
ctor: any,
newProps: any,
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): boolean {
// ...
const oldState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
let newState = (instance.state = oldState);
let updateQueue = workInProgress.updateQueue;
if (updateQueue !== null) {
// 遍历更新队列计算得到新值
processUpdateQueue(
workInProgress,
updateQueue,
newProps,
instance,
renderExpirationTime,
);
newState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
}
// ...
}
// ...
// 处理更新队列,返回新的 state
export function processUpdateQueue<State>(
workInProgress: Fiber,
queue: UpdateQueue<State>,
props: any,
instance: any,
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): void {
// ...
while (update !== null) {
// ...
{
resultState = getStateFromUpdate(
workInProgress,
queue,
update,
resultState,
props,
instance,
);
// 收集 callback,在 commit 阶段执行
const callback = update.callback;
if (callback !== null) {
workInProgress.effectTag |= Callback;
update.nextEffect = null;
if (queue.lastEffect === null) {
queue.firstEffect = queue.lastEffect = update;
} else {
queue.lastEffect.nextEffect = update;
queue.lastEffect = update;
}
}
}
// Continue to the next update.
update = update.next;
}
// ...
workInProgress.memoizedState = resultState;
// ...
}
// ...
function getStateFromUpdate (..., partialState, ...) {
// ...
if (typeof _payload2 === 'function') {
// ...
// Merge the partial state and the previous state.
return _assign({}, prevState, partialState);
}
}commit
该阶段又分为三个子阶段
before mutationmutationlayout
在第一个阶段,classComponent 会更新当前的 state 和 props(实际计算新值的操作在render阶段的beginWork中执行,并赋值给 fiber 节点的memorizedState和memorizedProps)
其中执行 setState 的 callback 发生在第三个阶段 layout,入口代码如下:
// react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberScheduler.js
// ...
while (nextEffect !== null) {
try {
commitAllLifeCycles(root, committedExpirationTime);
} catch (e) {
// ...
}
}
// ...commitAllLifeCycles 这个函数内主要调用了 commitLifeCycles
// react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactFiberCommitWork.js
function commitLifeCycles(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
current: Fiber | null,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedExpirationTime: ExpirationTime
): void {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
// ...
case ClassComponent: {
const instance = finishedWork.stateNode;
// ...
const updateQueue = finishedWork.updateQueue;
if (updateQueue !== null) {
// ...
commitUpdateQueue(
finishedWork,
updateQueue,
instance,
committedExpirationTime
);
}
return;
}
// ...
}
}commitUpdateQueue 会遍历更新队列执行 setState 的 callback
// react/packages/react-reconciler/src/ReactUpdateQueue.js
export function commitUpdateQueue<State>(
finishedWork: Fiber,
finishedQueue: UpdateQueue<State>,
instance: any,
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime
): void {
// If the finished render included captured updates, and there are still
// lower priority updates left over, we need to keep the captured updates
// in the queue so that they are rebased and not dropped once we process the
// queue again at the lower priority.
if (finishedQueue.firstCapturedUpdate !== null) {
// Join the captured update list to the end of the normal list.
if (finishedQueue.lastUpdate !== null) {
finishedQueue.lastUpdate.next = finishedQueue.firstCapturedUpdate;
finishedQueue.lastUpdate = finishedQueue.lastCapturedUpdate;
}
// Clear the list of captured updates.
finishedQueue.firstCapturedUpdate = finishedQueue.lastCapturedUpdate = null;
}
// Commit the effects
commitUpdateEffects(finishedQueue.firstEffect, instance);
finishedQueue.firstEffect = finishedQueue.lastEffect = null;
commitUpdateEffects(finishedQueue.firstCapturedEffect, instance);
finishedQueue.firstCapturedEffect = finishedQueue.lastCapturedEffect = null;
}
function commitUpdateEffects<State>(
effect: Update<State> | null,
instance: any
): void {
while (effect !== null) {
const callback = effect.callback;
if (callback !== null) {
effect.callback = null;
callCallback(callback, instance);
}
effect = effect.nextEffect;
}
}批量更新
在 react 15 是借助了事务和锁实现了批量更新,在 react 16 是怎么实现的呢?
比如我们触发了一个合成事件 onClick,会触发 dispatchEvent ,执行到 batchedUpdates 函数
function batchedUpdates<A, R>(fn: (a: A) => R, a: A): R {
const previousIsBatchingUpdates = isBatchingUpdates; // 默认是 false
isBatchingUpdates = true;
try {
return fn(a);
} finally {
isBatchingUpdates = previousIsBatchingUpdates;
if (!isBatchingUpdates && !isRendering) {
performSyncWork();
}
}
}这里同样是用了锁(isBatchingUpdates)来开启批量更新模式,所以如果我们在合成事件(fn)里面触发 多次setState,react 会根据 isBatchingEventUpdates = true 判断当前处于批量更新模式,会把更新任务挂载到更新队列上,当合成事件执行完毕后才统一调度更新
其他
react 17 和 react 16 其他版本,其实跟 react v16.8.3 实现 setState 的思路大同小异(后面有空再补上最新版本的)。大体上都是产生一个 update 对象去承载新的状态。多个 update 对象会连接成一个环状单向链表 - updateQueue 并挂载 fiber 上, 然后在更新该 fiber 的时候 (beginWork)会循环该 updateQueue,依次处理其中的 update,计算得到最新的 state