得闲翻下 react17 的源码和相关文章,学习一下 react 的 useState 的实现原理。整个过程蛮有趣的,首先得理解 fiber 架构,其次在 debugger 源码的时候得学习和理解一些必要的上下文,整体来说受益匪浅
前置知识
闭包
在 hooks 的应用比如 dispatch 函数,也就是 useState 返回的第二个参数
闭包是指有权访问另一个函数作用域中变量或方法的函数,创建闭包的方式就是在一个函数内创建闭包函数,通过闭包函数访问这个函数的局部变量, 利用闭包可以突破作用链域的特性,将函数内部的变量和方法传递到外部。
单链表
A—>B—>C。fiber 架构通过使用这种数据结构,实现了 render 过程的可中断性。比如更新了 B 节点,突然有高优先级插入,这个时候只需要记住当前更新到的节点是 B 即可,然后去执行高优任务,之后再从 B 节点继续更新
fiber & hook
fiber 对象和 hook 对象的关系如下图:
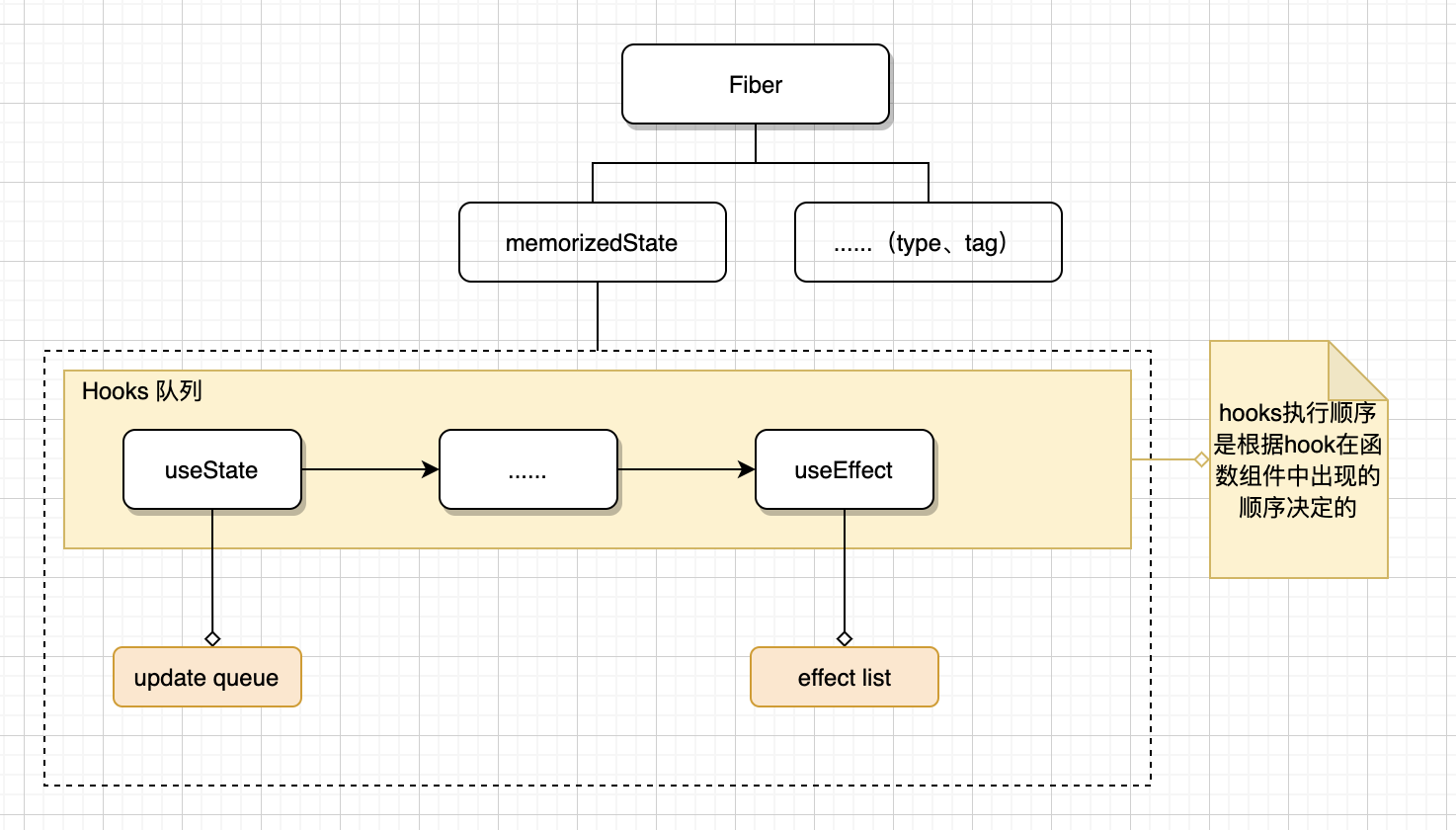
fiber 架构
React 16 引入了 fiber 架构,会基于 ReactElement 生成唯一的 fiber 对象。在更新阶段,会基于旧的 fiber 链表创建一个新的 fiber 链表(如下图),可以复用旧的对象,并且获取旧 hooks 的状态
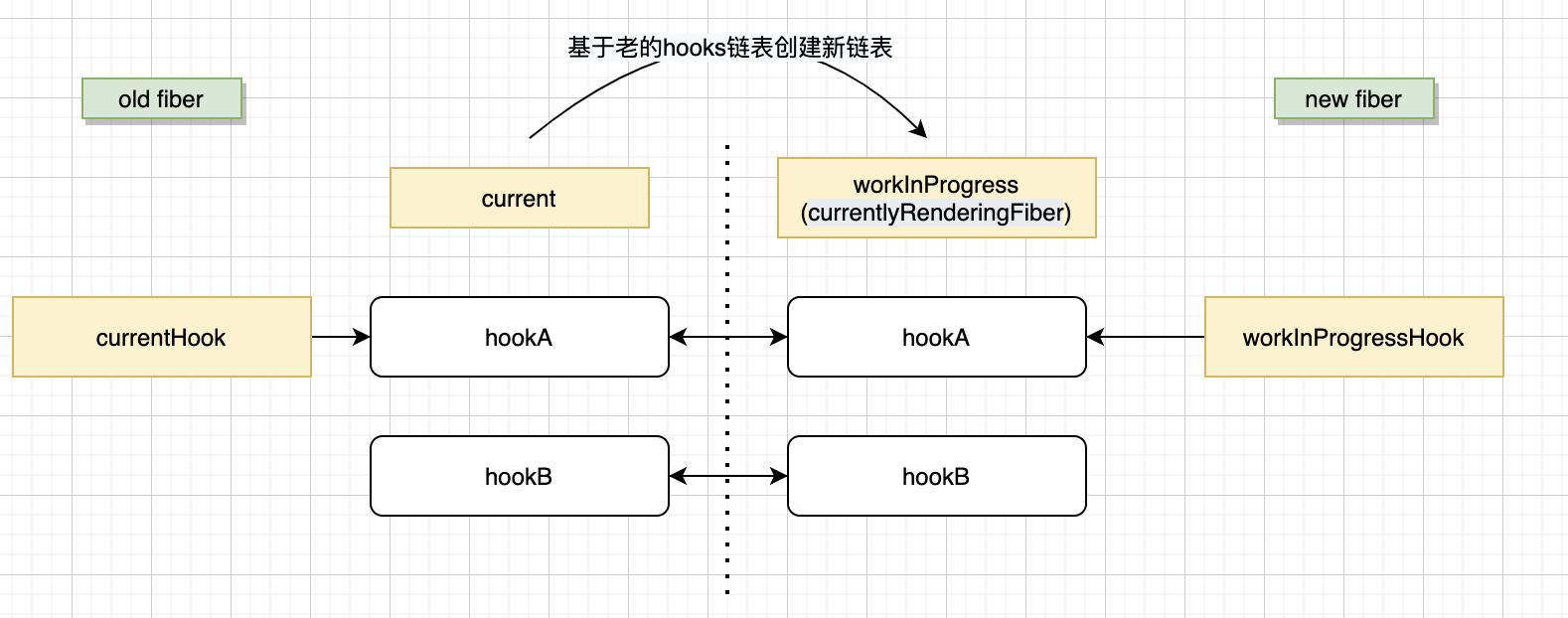
两个单链表
hooks 链表
/*
Hooks are stored as a linked list on the fiber's memoizedState field.
hooks 以链表的形式存储在fiber节点的memoizedState属性上
The current hook list is the list that belongs to the current fiber.
当前的hook链表就是当前正在遍历的fiber节点上的
The work-in-progress hook list is a new list that will be added to the work-in-progress fiber.
work-in-progress hook 就是即将被添加到正在遍历fiber节点的hooks新链表
*/
let currentHook: Hook | null = null;
let nextCurrentHook: Hook | null = null;无论是初次挂载还是更新,每调用一次 hooks 函数,都会产生一个 hook 对象与之对应,hook 对象结构如下
{
baseQueue: null, // 当前 update
baseState: 'hook1', // 初始值,即 useState 入参
memoizedState: null, // 当前状态(更新时表示上一次的状态)
queue: null, // 待执行的更新队列(queue.pending)
next: { // 下一个 hook
baseQueue: null,
baseState: null,
memoizedState: 'hook2',
next: null
queue: null
}
}产生的 hook 对象依次排列,形成链表存储到函数组件 fiber.memoizedState 上。在这个过程中,有一个十分重要的指针:workInProgressHook,它通过记录当前生成(更新)的 hook 对象,可以间接反映在组件中当前调用到哪个 hook 函数了。每调用一次 hook 函数,就将这个指针的指向移到该 hook 函数产生的 hook 对象上
比如先调用 hookA
fiber.memoizedState: hookA
^
workInProgressHook调用 hookB
fiber.memoizedState: hookA -> hookB
^
workInProgressHookhooks 的更新队列
这其实是个单链表环,存放某个 hook 的更新队列,如下图,是一个 useState 的更新队列:
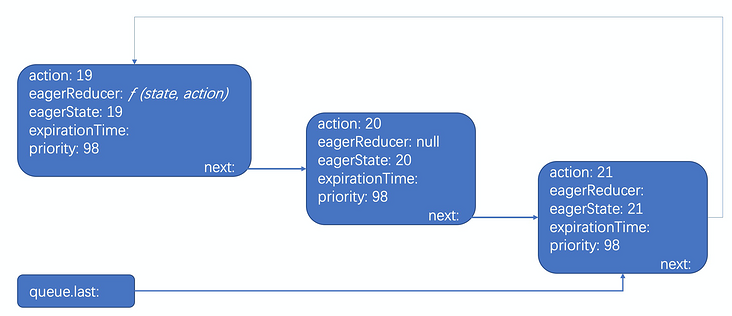
其实还有一个副作用链表,跟 useEffect 有关,最终会挂到 root 节点上
源码执行流程
renderWithHooks
对于函数组件(FunctionComponent)类型,在 beginwork 的时候会调用 renderWithHooks 注册,根据 mount 还是 update 调用一个函数生成 hooks 链表挂在 Fiber 上
// renderWithHooks
function renderWithHooks(current, workInProgress, Component, props, secondArg, nextRenderLanes) {
...
// 当前fiber
currentlyRenderingFiber$1 = workInProgress;
// hooks队列
workInProgress.memoizedState = null;
// 副作用队列
workInProgress.updateQueue = null;
{
if (current !== null && current.memoizedState !== null) {
ReactCurrentDispatcher$1.current = HooksDispatcherOnUpdateInDEV;
} else if (hookTypesDev !== null) {
ReactCurrentDispatcher$1.current = HooksDispatcherOnMountWithHookTypesInDEV;
} else {
ReactCurrentDispatcher$1.current = HooksDispatcherOnMountInDEV;
}
}
...
return children;
}mount
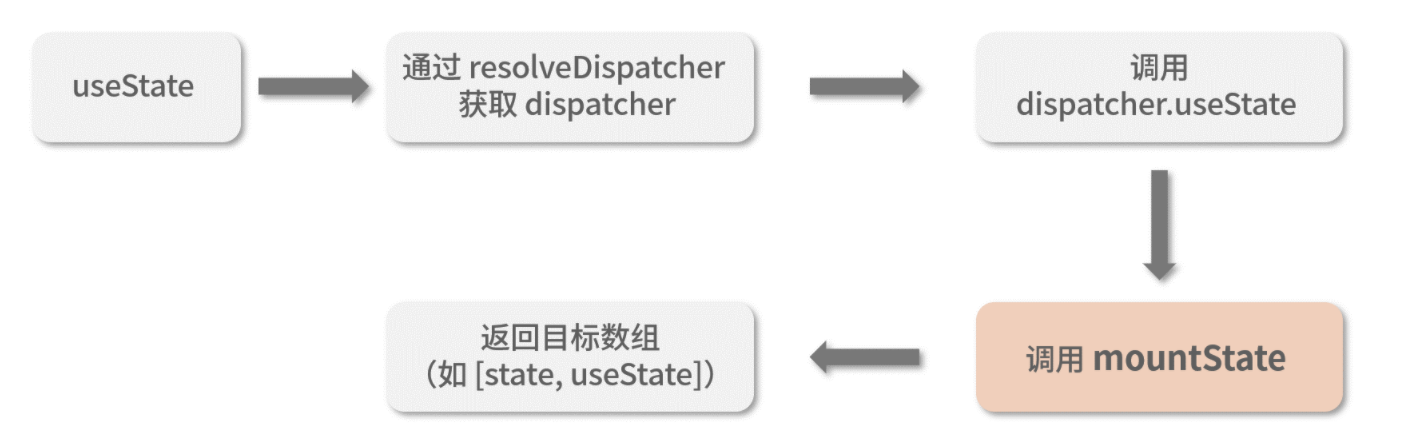
update
mount 阶段
/**
* ReactCurrentDispatcher 是一个内部储存状态的状态机.
* 主要作用还是用于切换不同执行时机的 dispatcher 对象
* */
const ReactCurrentDispatcher = { current: null };
function resolveDispatcher() {
const dispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher.current;
return dispatcher;
}
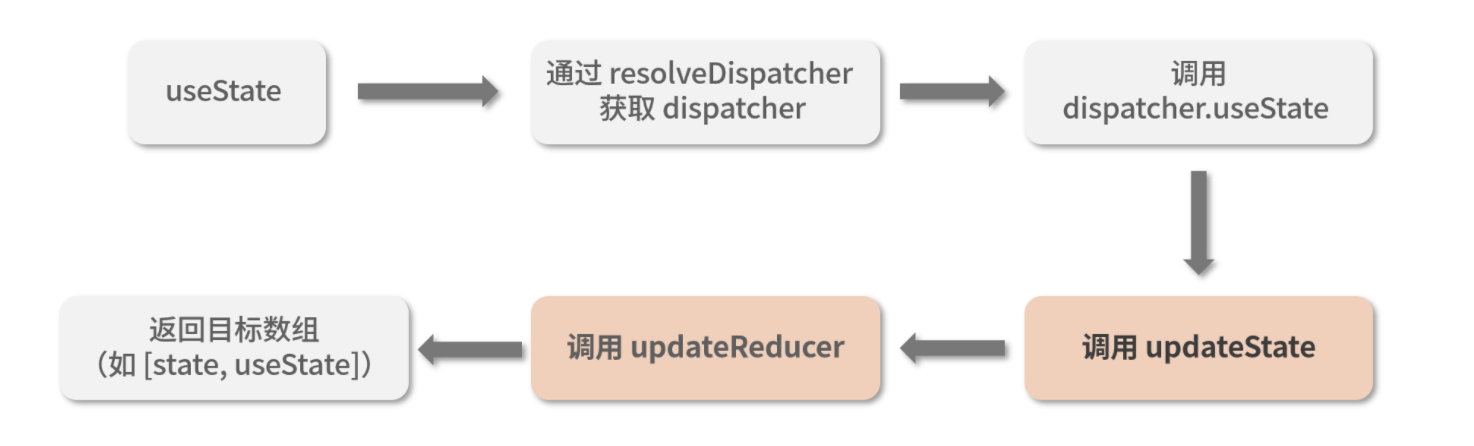
function useState(initialState) {
var dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useState(initialState);
}// resolveDispatcher
...
useState: function (initialState) {
...
try {
return mountState(initialState);
} finally {
ReactCurrentDispatcher$1.current = prevDispatcher;
}
},
...// mountWorkInProgressHook
function mountWorkInProgressHook() {
var hook = {
memoizedState: null,
baseState: null,
baseQueue: null,
queue: null,
next: null,
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
currentlyRenderingFiber$1.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = hook;
} else {
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
// mountState
function mountState(initialState) {
// 创建 hook 对象
var hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
if (typeof initialState === "function") {
initialState = initialState();
}
hook.memoizedState = hook.baseState = initialState;
var queue = (hook.queue = {
pending: null, // update 队列
dispatch: null, // 触发函数,会触发更新,useState返回值的第二个参数
lastRenderedReducer: basicStateReducer, // 最后一次使用的 reducer,初始化时使用最基础的 reducer
lastRenderedState: initialState, // 上一次的值,挂载阶段该值为初始值
});
var dispatch = (queue.dispatch = dispatchAction.bind(
null,
currentlyRenderingFiber$1,
queue
));
// dispatch是一个闭包函数
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}useState 默认使用的更新器是 basicStateReducer
function basicStateReducer(state, action) {
return typeof action === "function" ? action(state) : action;
}update 阶段
先执行 useState 返回的 dispatch 函数
// mountState
...
var dispatch = queue.dispatch = dispatchAction.bind(null, currentlyRenderingFiber$1, queue);
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];function dispatchAction(fiber, queue, action) {
...
// 更新对象,是一个链表节点
var update = {
lane: lane, // 优先级
action: action, // 新值,也就是 setState 传入的参数
next: null, // 指向下一个更新对象
eagerReducer: null, // 上一次使用的 reducer
eagerState: null, // 旧值
};
var pending = queue.pending;
if (pending === null) {
// 在队列上添加当前hook的首个更新对象,并保持循环
update.next = update;
} else {
// 非首个更新对象,会追加到更新队列之后
update.next = pending.next;
pending.next = update;
}
queue.pending = update;
// fiber.alternate 指向旧 fiber 链表
var alternate = fiber.alternate;
if (fiber === currentlyRenderingFiber$1 || alternate !== null && alternate === currentlyRenderingFiber$1) {
didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdateDuringThisPass = didScheduleRenderPhaseUpdate = true;
} else {
if (fiber.lanes === NoLanes && (alternate === null || alternate.lanes === NoLanes)) {
var lastRenderedReducer = queue.lastRenderedReducer;
if (lastRenderedReducer !== null) {
var prevDispatcher;
{
// NOTE 暂不清楚这一步的作用
prevDispatcher = ReactCurrentDispatcher$1.current;
ReactCurrentDispatcher$1.current = InvalidNestedHooksDispatcherOnUpdateInDEV;
}
try {
var currentState = queue.lastRenderedState;
// 计算新的 state
var eagerState = lastRenderedReducer(currentState, action);
update.eagerReducer = lastRenderedReducer;
update.eagerState = eagerState;
if (objectIs(eagerState, currentState)) {
// 前后值没变,没必要更新
return;
}
} catch (error) {
// Suppress the error. It will throw again in the render phase.
} finally {
{
ReactCurrentDispatcher$1.current = prevDispatcher;
}
}
}
}
...
// 发起一次调度更新
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);
}
}更新 WorkInProgressHook
function updateWorkInProgressHook() {
var nextCurrentHook;
if (currentHook === null) {
var current = currentlyRenderingFiber$1.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
nextCurrentHook = current.memoizedState;
} else {
nextCurrentHook = null;
}
} else {
nextCurrentHook = currentHook.next;
}
var nextWorkInProgressHook;
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
nextWorkInProgressHook = currentlyRenderingFiber$1.memoizedState;
} else {
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
}
if (nextWorkInProgressHook !== null) {
workInProgressHook = nextWorkInProgressHook;
nextWorkInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next;
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
} else {
...
currentHook = nextCurrentHook;
var newHook = {
memoizedState: currentHook.memoizedState,
baseState: currentHook.baseState,
baseQueue: currentHook.baseQueue,
queue: currentHook.queue,
next: null
};
if (workInProgressHook === null) {
currentlyRenderingFiber$1.memoizedState = workInProgressHook = newHook;
} else {
workInProgressHook = workInProgressHook.next = newHook;
}
}
return workInProgressHook;
}真正得到最终状态,其实是在下一次获取状态的时候。
更新阶段开始时,同样会执行 renderWithHooks,此时会将 ReactCurrentDispatcher.current 指向 HooksDispatcherOnUpdate 对象
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = {
...
useState: updateState,
}
function updateState(initialState) {
return updateReducer(basicStateReducer, initialState);
}
...
// updateReducer
function updateReducer(reducer, initialArg, init) {
var hook = updateWorkInProgressHook();
var queue = hook.queue;
...
do {
...
if (update.eagerReducer === reducer) {
newState = update.eagerState;
} else {
// 遍历更新队列,得到最新值
var action = update.action;
newState = reducer(newState, action);
}
...
update = update.next;
} while (update !== null && update !== first);
...
var dispatch = queue.dispatch;
return [hook.memoizedState, dispatch];
}简单总结一下 update 的过程:
- 调用
dispatcher函数 - 收集
update,将update对象按序插入更新队列queue.pending - 调度一次 React 的更新
- 重新执行组件函数时,
useState会被重新执行,在resolve dispatcher的阶段取到负责更新的dispatcher - 按序执行更新队列,拿到最新的
state - 渲染真实 DOM,更新结束
其他问题
为什么在 React 16 前,函数式组件不能拥有状态管理?
因为 16 以前只有类组件在更新时存在实例,而 16 以后 Fiber 架构的出现,让每一个节点都拥有对应的实例,也就拥有了保存状态的能力
为什么只能在函数组件中使用 hooks?
只有函数组件才走 renderWithHooks 的逻辑
为什么 hooks 不能在循环、判断语句中调用,而只能在函数最外层使用?
因为在更新时,这个队列需要是一致的,才能保证 hooks 的结果正确。
useState 的 setState 是同步操作还是异步操作?
默认是异步。从上面的源码分析可以看出,执行 setState 时会将更新对象(update)存入更新队列,等到 commit 阶段才会一次性执行该更新队列。在没有重新执行 app 函数时,拿到的始终是旧状态,所以就造成了异步的现象
连续执行同一个 setState,会造成多次渲染吗?比如下面这段代码:
onClick = () => {
setState(0);
setState(1);
setState(2);
};不会。执行事件函数时,会判断当前是否处于批量更新(具体逻辑可以参见 scheduleUpdateOnFiber 源码),如果处于批量更新状态,说明还不能重新渲染,需要等待该状态结束(比如 react 中的 onClick 事件)。在批量更新阶段,每个 hooks 会通过 queue 将更新(update)存入更新队列(单链表)中,这个队列会保证更新顺序。等到批量更新状态结束了,才会重新执行组件函数,之后执行到对应 hook 时,会一次性执行挂载在 hook 上的更新队列,从而更新状态。
执行两次 setState(0) 会执行两次函数组件吗?
不会。在更新时会通过 ObjectIs 判断更新前后的值是否变化,如果没变化是不会调度更新的